From data breaches to the dark web, fraudsters are exploiting unprecedented opportunities
SAS, The COVID-19 pandemic’s economic fallout has threatened the livelihoods of millions of Americans. However, it has been a windfall for criminals who take advantage of those who need help the most.
Coming off historically low unemployment rates, unemployment insurance (UI) agencies found themselves understaffed and ill-prepared for the claims tsunami caused by the pandemic. Additionally, the CARES Act loosened controls in order to quickly get money out the door. While this was important for urgently getting assistance to those in need, it exposed agencies to fraud perpetrated by organized criminal networks at a scale never seen before, overwhelming fraud prevention efforts.
Read More: With CallRail’s New Lead Center, SMBs Will Never Miss A Lead Again
How identity theft is fueling unemployment fraud
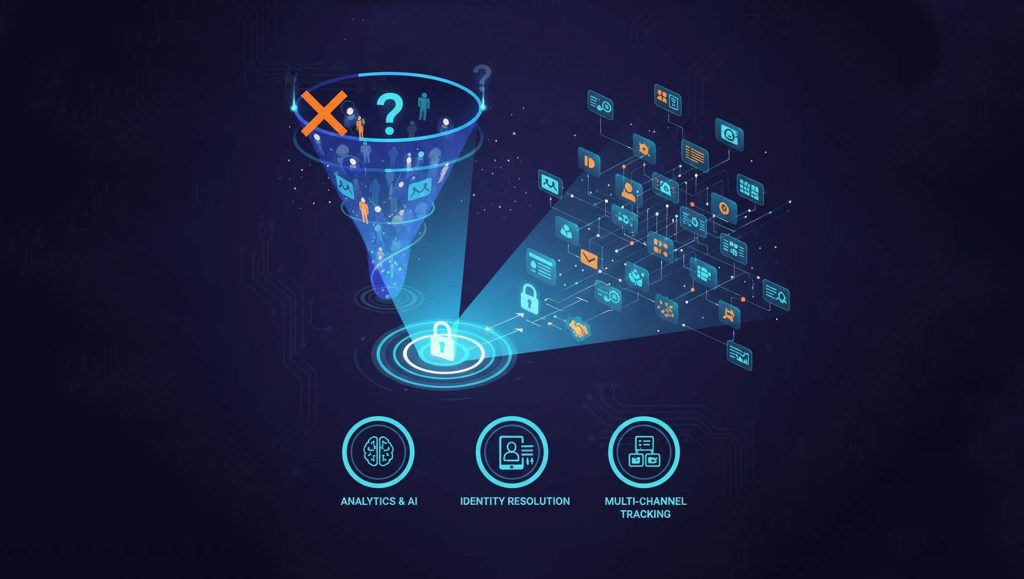
One of the most common tactics of fraudsters is the use of stolen identity credentials such as names, Social Security numbers and addresses to file claims and open accounts on another person’s behalf, then redirect funds to themselves. In many cases, identity thieves sit on vast amounts of stolen credentials, waiting for the perfect opportunity to pounce. COVID-19 has been an opportunity like no other. But for many of the fraudulent claims, the identity theft-to-fraud process began much earlier.
Here are the four steps of identity theft and fraud:
- First there is a data breach. We know that billions of personal records are exposed annually. A recent RiskIQ study found that more than 16,000 records per minute were compromised in 2020. In the first half of 2020 alone, Twitter, Marriott, MGM Resorts and Zoom all suffered data breaches.
- Next, personal records are sold on the dark web. What is the dark web? Alongside the internet most of us experience, lies a mammoth archive of unindexed material called the deep web, and a well-concealed part of the deep web called the dark web. The secret nature of the dark web has helped it become an identity theft marketplace, where bad actors can buy and sell personal information in nearly complete anonymity. Billions of stolen identity records are available for surprisingly low prices. A Social Security number can sell for as little as $1 and a credit/debit card number for $5. A person’s full information set costs around $8.
- Then comes the actual identity theft. One in four people who are notified their information may have been exposed in a data breach actually have their identities stolen. Considering that most have had their data compromised multiple times, this nets out to about one person having their identity stolen every three seconds. Surprisingly, having personal data stolen and then sold on the dark web does not equate to identity theft. Identity theft doesn’t occur until that stolen information is used for financial gain.
- Those financial gain opportunities often come in the form of government programs. According to the Federal Trade Commission, government fraud accounts for 22% of all identity theft, second only to banking fraud. However, that data is from before the pandemic. Since we know fraudsters have been increasingly targeting government programs in 2020, it is likely to be much higher now.
Read More: Prophix Taps Susan Gershman As Company’s First Chief Customer Innovation Officer